Recreating arXiv Citation Graph using Recurrent Neural Networks
Semester Thesis at the Chair for Mathematical Information Science, ETH Zürich under Prof. Dr. Helmut Bölcskei.
Oveview
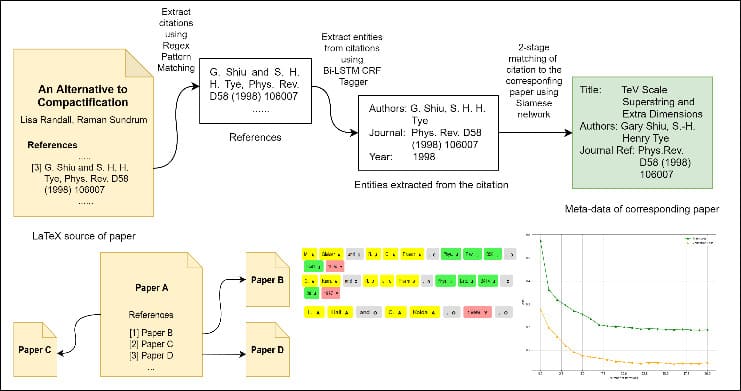
The usefulness of a bibliographic database depends highly on a consistent citation graph which links the papers present in the database. Owing to the large variations in citation formats used for listing bibliographic information, it has become an increasingly difficult problem to accurately find the corresponding cited papers. In this work, we make an attempt towards recreating arXiv citation graph using only the raw LaTeX dump of research articles. We present a novel generalised pipeline which employs a combination of traditional heuristics and modern deep learning methods to find the list of papers cited by an article. The proposed 3-stage pipeline is illustrated in figure below.

We evaluate the results of the pipeline on the datasets provided in the data cleaning task of the KDD Cup 2003 which comprises a collection of over 35,000 articles submitted in the hep-ph (High Energy Physics - Phenomenology) section of arXiv between 1992 and 2003. Our pipeline extracts around 285k edges present in the hep-ph citation graph correctly out of 421k edges present in the true citation graph. This achieves an accuracy of around 95% while matching citations to the corresponding article and outperforms the top solutions presented in KDD Cup 2003 by a large margin with a 64% relative improvement in symmetric difference size. To validate the generality of the approach, we also report empirical results of the pipeline over another dataset presented in the same challenge for citation prediction task, which contains around 29,000 hep-th (High Energy Physics - Theory) papers submitted on arXiv. Detailed results can be found here.
Important Links
KDD Cup 2003
KDD Cup Overview
Report
Bidirectional LSTM-CRF Models for Sequence Tagging